[ad_1]
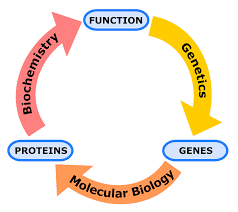
Genetics and Molecular Biology are closely related fields that focus on the study of genes, heredity, and the molecular mechanisms that govern biological processes. Here’s some information about each field:
Genetics: Genetics is the study of genes, heredity, and the variation of inherited traits in living organisms. It involves the understanding of how genes are passed from one generation to another and how they contribute to the development and functioning of organisms. Key aspects of genetics include:
Mendelian Genetics: Mendelian genetics explores the principles of inheritance based on the work of Gregor Mendel. It involves studying traits, alleles, genotype, phenotype, Punnett squares, and genetic crosses.
Molecular Genetics: Molecular genetics focuses on the study of genes at the molecular level. It involves understanding the structure and function of genes, DNA replication, transcription, and translation processes.
Population Genetics: Population genetics examines the genetic variation within populations and how it changes over time. It investigates factors such as genetic drift, gene flow, natural selection, and genetic adaptation.
Human Genetics: Human genetics focuses on the study of genetic traits, diseases, and conditions in humans. It involves the identification of genetic disorders, genetic counseling, and the use of genetic technologies in medical research and diagnosis.
Molecular Biology: Molecular biology is the study of biological processes at the molecular level, particularly the structure, function, and interactions of biomolecules within cells. It involves investigating the mechanisms by which DNA, RNA, proteins, and other molecules control cellular functions. Key aspects of molecular biology include:
DNA Structure and Replication: Molecular biology explores the double helix structure of DNA, its replication, and the enzymes involved in DNA replication and repair processes.
Gene Expression: Gene expression involves the activation and regulation of genes to produce functional proteins. It includes transcription, RNA processing, and translation processes.
Genetic Engineering: Genetic engineering uses techniques to manipulate and modify genes for various purposes. It includes the insertion of genes into organisms, the creation of transgenic organisms, and the production of recombinant proteins.
Genomics: Genomics involves the study of entire genomes, including the sequencing and analysis of DNA. It aims to understand the structure, function, and evolution of genes and genomes.
Molecular Genetics Techniques: Molecular biology utilizes various techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA sequencing, gel electrophoresis, gene cloning, and gene expression analysis to investigate molecular processes.
Molecular Evolution: Molecular evolution examines the changes in DNA and protein sequences over time to understand the evolutionary relationships among species and the mechanisms driving evolutionary change.
Molecular Medicine: Molecular biology contributes to medical research and the development of treatments for genetic diseases. It involves studying the molecular basis of diseases, identifying genetic markers, and developing targeted therapies.
#Genetics
#MolecularBiology
#Genomics
#GeneExpression
#DNAReplication
#GeneticEngineering
#MolecularGenetics
#GeneticResearch
#GeneticDiseases
#MolecularMedicine
#Transcription
#Translation
#GeneticCounseling
#PopulationGenetics
#MolecularEvolution
[ad_2]
Source link